Topic: Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic Spectrum
In which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is the maximum intensity of Earth’s outgoing radiation?
(1) visible light
(2) gamma rays
(3) infrared
(4) ultraviolet

This Doppler radar instrument transmits electromagnetic energy in the form of microwaves. Some microwave wavelengths are between the wavelengths of
(1) gamma rays and x rays
(2) infrared and radio waves
(3) ultraviolet and infrared
(4) x rays and ultraviolet
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble’s discovery of a pattern in the red shift of light from galaxies moving away from Earth led to the theory of an expanding universe. This expansion implies that the universe was smaller, denser, and hotter in the past. In the 1940s, scientists predicted that heat (identified as cosmic microwave background radiation) left over from the Big Bang would fill the universe. In the 1960s, satellite probes found that cosmic microwave background radiation fills the universe uniformly in every direction, and indicated a temperature of about 3 kelvins (K). This radiation has been cooling as the universe has been expanding.
Cosmic microwave background radiation is classified as a form of electromagnetic energy because it
(1) travels in waves through space
(2) moves faster than the speed of light
(3) is visible to humans
(4) moves due to particle collisions
Most of the electromagnetic energy radiated from Earth’s surface is in the form of
(1) ultraviolet rays
(2) infrared rays
(3) gamma rays
(4) x rays
Most of which type of electromagnetic radiation is given off by Earth’s surface at night?
(1) gamma rays
(2) ultraviolet light
(3) visible light
(4) infrared rays
Most of the long-wave energy radiated from Earth and lost to space on a cloudless night is
(1) ultraviolet
(2) infrared
(3) visible light
(4) gamma rays
Which type of electromagnetic radiation listed below has the longest wavelength?
(1) infrared
(2) ultraviolet
(3) red visible light
(4) violet visible light

Write the chemical symbol for the element, shown in the table, that absorbs the two wavelengths of light. [1]
Allow 1 credit for Ca.
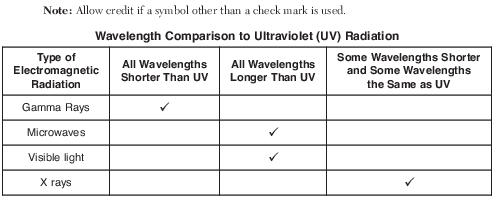
On the table in the image provided, place one check mark in each row to compare the relative wavelengths of other types of electromagnetic radiation to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. [1]
Wavelength Comparison to Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
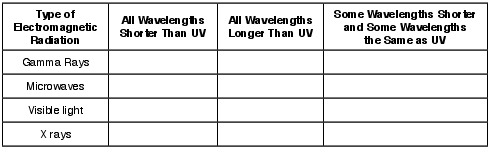
Allow 1 credit for a correctly completed chart as shown below.
•